规模化敏捷LeSS 与 LeSS Huge框架规则 (Large Scale Scrum)

敏捷宣言与敏捷原则中文版
2016年9月8日
生态系统因果图系统思考Casual Loop Diagram-狼图腾节选
2016年9月15日目录
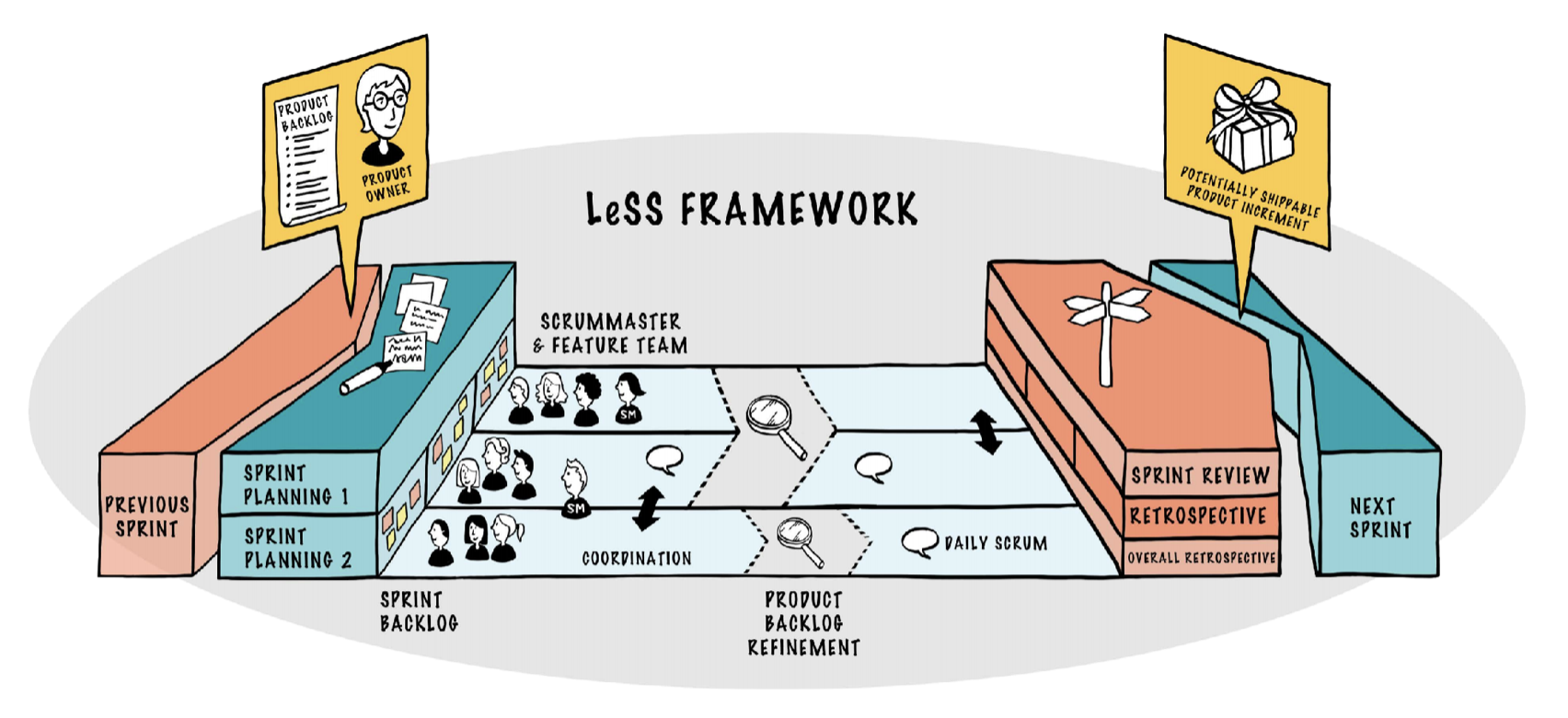
LeSS框架规则
LeSS框架规则应用于2-“8”个团队的产品。
LeSS介绍视频
正在加载视频,如果长时间未显示,请刷新页面
LeSS结构
- 用团队作为基本模块来构建组织
- 每个团队是:1)自管理的、2)跨职能的、3)同在一地的、4)长期的
- 多数团队都是以客户为中心的特性团队
- Scrum Master负责一个运转良好的LeSS导入。他们关注于团队、产品所有人、组织和开发实践。一个Scrum Master不只关注一个团队,而是整个组织系统。
- Scrum Master是一份专职和全职工作
- 一个Scrum Master可以服务1-3个团队
- 在LeSS里,管理者是可选的,但是如果管理者还存在的话他们的角色可能会改变。他们的焦点从管理日常产品工作转向改进产品开发系统的价值交付能力
- 管理者的角色是通过实践“开展现场调查”、鼓励停下来修正,以及“试验高于遵循”来改进产品开发系统
- 对产品组从一开始就建立完整的LeSS结构,这个对LeSS导入至关重要
- 对超越产品组的更大组织,采用“开展现场调查”来演进地导入LeSS,从而创建一个以试验和改进为常态的组织
LeSS产品
- 对整个可以交付的产品有一个产品所有人和一个产品待办列表
- 产品所有人不应该独自工作于产品待办列表的梳理;他通过让多个团队直接和客户/用户以及干系人工作来获得支持
- 所有的优先级排序都通过产品所有人,但是澄清尽量由团队和客户/用户以及干系人直接进行
- 产品的定义应该是在实际的前提下尽量广并且以终端用户/客户为导向。随着时间的推移,产品的定义可能会扩大。我们倾向于更广的定义
- 对整个产品有一个所有团队一致的完成的定义
- 每个团队可以扩展共同的定义以形成自己团队的更为严格的完成的定义
- 完美的目标是通过改进完成的定义达到每个Sprint都产出可交付的产品(或者更为频繁)
LeSS Sprint
- 有一个产品层面的Sprint,而不是每个团队有不同的Sprint。每个团队同时开始和结束一个Sprint。每个Sprint产出一个集成的完整产品
- Sprint计划由两部分组成:Sprint计划第一部分是所有团队共同做,而Sprint计划第二部分通常由各团队分别做。对那些相关性强的条目在一个共享空间内做多团队的Sprint计划第二部分
- Sprint计划第一部分由产品所有人和团队代表参加。他们一起试探性地选择每个团队将在下一个Sprint工作的条目。团队会去识别一起合作的机会,并澄清最终的问题
- 每个团队有自己的Sprint待办列表
- Sprint计划第二部分是让团队决定怎么做选了的条目。这通常涉及设计并产生他们的Sprint待办列表
- 每个团队有自己的每日站会
- 跨团队协调由团队决定。倾向于分布式和非正式协调而非集中式协调。强调实时交流和非正式的网络,采用代码交流、跨团队会议、组件导师、旅行者、侦察员和开放空间
- 产品待办列表梳理由每个团队对自己可能接下来要做的条目进行。举行多团队和/或者整体的产品待办列表梳理来增加共享的理解,并当有紧密关联的条目或者有需要更广范围进行输入和学习时发现协调机会加以利用
- 有一个产品的Sprint评审;对所有团队都是共同的。确保足够的干系人能够参加并贡献有效检验和适应所需要的信息。
- 每个团队有自己的Sprint回顾
- 在团队各自的回顾之后举行一个整体的回顾来讨论跨团队和系统性的问题,并创建改进试验。这个会议由产品所有人、Scrum Master们、团队代表和管理者(如果有的话)参加。
LeSS巨型框架规则
LeSS巨型框架应用于“8”个以上团队的产品。避免在小型产品组上应用LeSS巨型框架,因为这会带来更多的开销和局部优化。
如果没有特别指出,所有LeSS规则都应用于LeSS巨型框架。每个需求领域就象一个基本的LeSS框架。
LeSS巨型结构
- 从客户角度强相关的客户需求会以需求领域分组
- 每个团队专攻一个需求领域。团队会长期固定于某个领域,但是当其它领域的价值变得更高时,团队也可能改变其工作的需求领域
- 每个需求领域有一个领域产品所有人
- 每个需求领域有“4-8”个团队。避免超出这个范围
- LeSS巨型的导入,包括其结构变化,是以演进增量式的方式发生的
- 每天都记得:LeSS巨型的导入会需要很多个月或者年、很多的耐心、还有一些幽默感
LeSS巨型产品
- 每个需求领域有一个领域产品所有人
- 有一个整体的产品所有人来负责产品层面的优先级排序和决定哪些团队工作在哪个领域。他和领域产品所有人紧密地工作在一起
- 领域产品所有人对他们的团队来说就是产品所有人
- 有一份产品待办列表;里面的每个条目只属于一个需求领域
- 每个需求领域有一份领域产品待办列表。这个列表概念上来说是整个产品待办列表更细粒度的视角
LeSS巨型Sprint
- 有一个产品层面的Sprint,而不是针对需求领域有不同的Sprint。这样每个Sprint会带来一个集成的整体产品
- 产品所有人和领域产品所有人会频繁同步。在Sprint计划前他们确保团队都工作在最有价值的条目上。在Sprint评审后,他们在产品层面做出适应。
LeSS Framework Rules
The LeSS framework applies to products with 2-“8” teams.
LeSS Structure
- Structure the organization using real teams as the basic organizational building block.
- Each team is (1) self-managing, (2) cross-functional, (3) co-located, and (4) long-lived.
- The majority of the teams are customer-focused feature teams.
- Scrum Masters are responsible for a well-working LeSS adoption. Their focus is towards the Teams, Product Owner, organization, and development practices. A Scrum Master does not focus on just one team but on the overall organizational system.
- A Scrum Master is a dedicated full-time role.
- One Scrum Master can serve 1-3 teams.
- In LeSS, managers are optional, but if managers do exist their role is likely to change. Their focus shifts from managing the day-to-day product work to improving the value-delivering capability of the product development system.
- Managers’ role is to improve the product development system by practicing Go See, encouraging Stop & Fix, and “experiments over conformance”.
- For the product group, establish the complete LeSS structure “at the start”; this is vital for a LeSS adoption.
- For the larger organization beyond the product group, adopt LeSS evolutionarily using Go and See to create an organization where experimentation and improvement is the norm.
LeSS Product
- There is one Product Owner and one Product Backlog for the complete shippable product.
- The Product Owner shouldn’t work alone on Product Backlog refinement; he is supported by the multiple Teams working directly with customers/users and other stakeholders.
- All prioritization goes through the Product Owner, but clarification is as much as possible directly between the Teams and customer/users and other stakeholders.
- The definition of product should be as broad and end-user/customer centric as is practical. Over time, the definition of product might expand. Broader definitions are preferred.
- One Definition of Done for the whole product common for all teams.
- Each team can have their own stronger Definition of Done by expanding the common one.
- The perfection goal is to improve the Definition of Done so that it results in a shippable product each Sprint (or even more frequently).
LeSS Sprint
- There is one product-level Sprint, not a different Sprint for each Team. Each Team starts and ends the Sprint at the same time. Each Sprint results in an integrated whole product.
- Sprint Planning consists of two parts: Sprint Planning One is common for all teams while Sprint Planning Two is usually done separately for each team. Do multi-team Sprint Planning Two in a shared space for closely related items.
- Sprint Planning One is attended by the Product Owner and Teams or Team representatives. They together tentatively select the items that each team will work on that Sprint. The Teams identify opportunities to work together and final questions are clarified.
- Each Team has their own Sprint Backlog.
- Sprint Planning Two is for Teams to decide how they will do the selected items. This usually involves design and the creation of their Sprint Backlogs.
- Each Team has their own Daily Scrum.
- Cross-team coordination is decided by the teams. Prefer decentralized and informal coordination over centralized coordination. Emphasize Just Talk and informal networks via communicate in code, cross-team meetings, component mentors, travelers, scouts, and open spaces.
- Product Backlog Refinement (PBR) is done per team for the items they are likely going to do in the future. Do multi-team and/or overall PBR to increase shared understanding and exploiting coordination opportunities when having closely related items or a need for broader input/learning
- There is one product Sprint Review; it is common for all teams. Ensure that suitable stakeholders join to contribute the information needed for effective inspection and adaptation.
- Each Team has their own Sprint Retrospective.
- An Overall Retrospective is held after the Team Retrospectives to discuss cross-team and system-wide issues, and create improvement experiments. This is attended by Product Owner, Scrum Masters, Team representatives, and managers (if any).
LeSS Huge Framework Rules
LeSS Huge applies to products with “8+” teams. Avoid applying LeSS Huge for smaller product groups as it will result in more overhead and local optimizations.
All LeSS rules apply to LeSS Huge, unless otherwise stated. Each Requirement Area acts like the basic LeSS framework.
LeSS Huge Structure
- Customer requirements that are strongly related from a customer perspective are grouped in Requirement Areas.
- Each Team specializes in one Requirement Area. Teams stay in one area for a long time. When there is more value in other areas, teams might change Requirement Area
- Each Requirement Area has one Area Product Owner.
- Each Requirement Area has between “4-8” teams. Avoid violating this range.
- LeSS Huge adoptions, including the structural changes, are done with an evolutionary incremental approach.
- Remember each day: LeSS Huge adoptions take months or years, infinite patience, and sense of humor.
LeSS Huge Product
- Each Requirement Area has one Area Product Owner.
- One (overall) Product Owner is responsible for product-wide prioritization and deciding which teams work in which Area. He works closely with Area Product Owners.
- Area Product Owners act as Product Owners towards their teams.
- There is one Product Backlog; every item in it belongs to exactly one Requirement Area.
- There is one Area Product Backlog per Requirement Area. This backlog is conceptually a more granular view onto the one Product Backlog.
LeSS Huge Sprint
- There is one product-level Sprint, not a different Sprint for each Requirement Area. It ends in one integrated whole product.
- The Product Owner and Area Product Owners synchronize frequently. Before Sprint Planning they ensure the Teams work on the most valuable items. After the Sprint Review, they further enable product-level adaptations.